Peng Lu and his colleagues explored Individual behaviors, social learning, and swarm intelligence by using a real case and counterfactuals
November 30, 2022, Prof. Peng Lu and his colleagues published a paper on Expert Systems With Applications. In this paper, they use the mass shooting case, as a typical category of common risks (social disasters), and use two-round simulations to achieve the research goal which is to calculate social knowledge, based on which social welfare can be enhanced, and to use social knowledge to improve social welfare.

Abstract:It is hard for individuals to handle social common risk, such as terrorism attacks (mass shooting). However, it can be contained, if they can be organized and behave intelligently. To obtain this swarm intelligence pattern, social knowledge should be captured to guide behaviors of isolated individuals. Here, we explore how swarm intelligence can be achieved by individual behaviors during social learning process. We have solved two issues. The first is to obtain social knowledge. Based on agent-based model of real target case, we calculate the optimal solution based on which we infer outcomes of all possible situations. Then, the matrix of social knowledge can be formed; The second is social learning process of individuals. Guided by the social knowledge, they all know that others will be mobilized as well. The key information is the minimal valid size of heroes, and all social members know that this condition is not difficult to satisfy. Thus, more individuals will be mobilized and become the Heroes to fight bravely against the shooter(s). Comparing two patterns, we obtain precise outcomes of how social losses (civilian deaths and injuries) can be reduced. Therefore, guided by clear social knowledge, social welfare can be enhanced substantially.
Keywords: Social knowledge;Agent-based model;Swarm intelligence;Counterfactuals
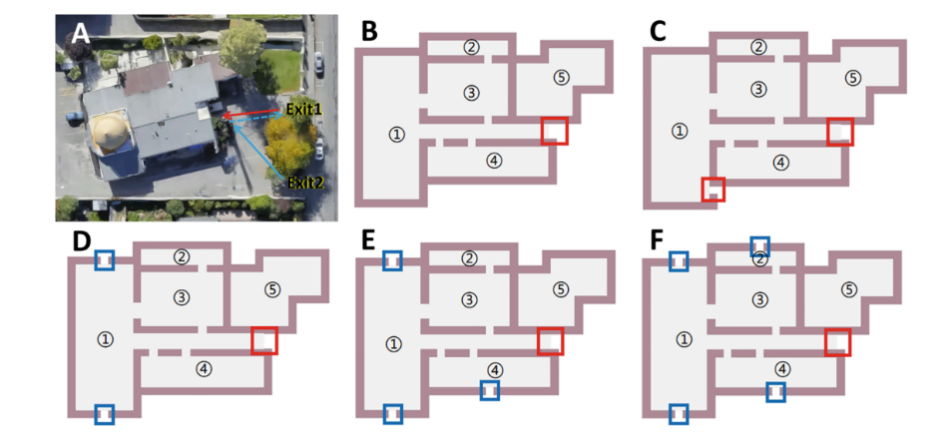
Fig. 1. Real case and other scenarios settings. Panel A is real scene, and the shooter entered and fired through exit 1. The red line refers to first round of shooting, and blue solid line refers to second-round of shooting. The blue dashed line is the retreat route of the shooter. Subfigures B-F refer to 5 counterfactual settings. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
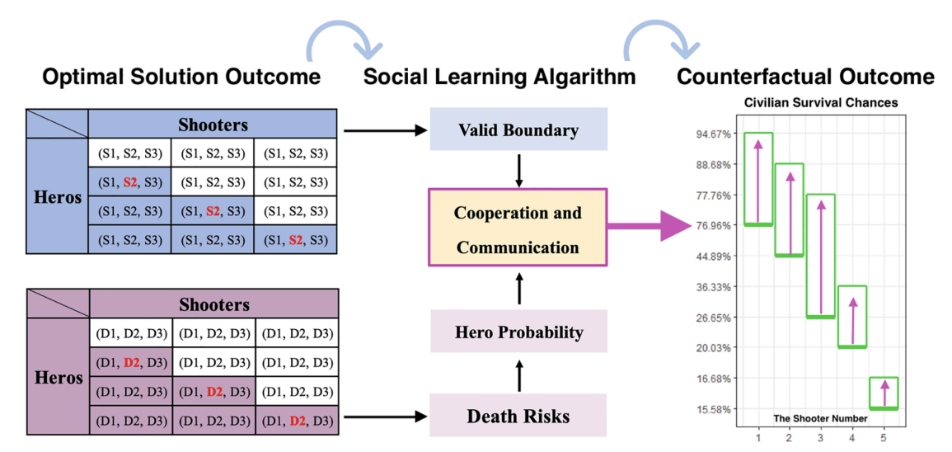
Fig. 2. Social Learning Algorithm. The blue matrix is the payoff matrix, with values of survival chances (rates) for three groups. The purple matrix is the risk matrix, with values death risks for three groups. The two matrices are complementary for each other. Both valid boundary and death risks will increase the probability of civilians to be the hero. After social learning, the survival chances (rates) of civilians will be enhanced, which is indicated by the boxplot (K-line diagram). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
2022年11月30日,国际权威学术期刊《Expert Systems with Applications》第207在线发表吕鹏和合作者的研究论文“Individual behaviors, social learning, and swarm intelligence: Real case and counterfactuals”。
该论文主要研究目标是证实:在社会知识的指导下,个体会做出群体智能行为,从而实现社会最优。为了实现这一目标,该论文认为应该在社会中加强社会学习过程,从而促进社会知识的形成。对于社会来说,这种社会学习算法应该在所有社区制度化。这样一来,社会成员将越来越了解社会知识,社会的英雄主义精神将得到进一步鼓励和加强。此外,社会知识可以是动态的。如果社会中亲社会人群的百分比增加了(因为加强了社会学习过程),社会知识矩阵将会被更新。然后,社会成员将在这种新的(更新的)社会知识下行动,从而产生新的社会结果。未来,研究团队将致力于发展(多轮)社会学习算法,其核心也是通过个人优化实现社会优化。
本论文的研究意义和价值在于:一方面,相关案例分析结果和结论丰富了人们对个体行为、社会学习与群体智能的理解,开发了社会学习算法;另一方面,其利用计算社会知识从而提高社会福利的目标也为社会管理者对于社会福利与社会保障的设计提供了重要的线索和启示。
Citation:
Lu Peng, et al.”Individual behaviors, social learning, and swarm intelligence: Real case and counterfactuals.” Expert Systems With Applications 207.(2022). doi:10.1016/J.ESWA.2022.117878.